Critical Patient Identification Points in Hospitals: The Value of Biometrics
Correct patient identification is essential for ensuring patient safety during medical care. In critical procedures such as admissions, blood transfusions, or radiotherapy, even a small error can have serious consequences. Implementing biometrics offers precise identification that protects the patient, reduces risks, and builds greater confidence throughout the entire care process.
In hospitals, patient safety largely depends on one fundamental factor: correct identification. Although it may seem like a simple process, an error in this step can have serious consequences, from misdiagnoses to wrong treatment being administered. According to The World Health Organization (WHO), millions of patients worldwide suffer harm each year due to medical errors, and a significant portion of these incidents are linked to identification errors.
Traditional methods, such as wristbands or manual checks, have been used for years, but they have limitations that make them vulnerable to human error, physical wear and tear, or even fraud. Faced with these risks, biometrics emerges as an advanced and reliable solution to ensure unequivocal identification during the highest-risk moments within a hospital. You can find more information about this in our article Patient identification in the healthcare environment.
What are the critical Patient Identification Points in Hospitals?
Patient identification should be present at all levels of care, but not all processes require the same level of rigor. There are critical points where any error can have irreversible consequences for the patient’s health and, consequently, for the reputation of the healthcare institution.
In these scenarios, biometrics provides a fundamental advantage: it ensures that each patient’s identity is unequivocally linked to their medical history, reducing the possibility of human error. By using technologies such as iris or fingerprint recognition, a level of precision is achieved that far surpasses traditional methods.
Biometrics can be integrated into multiple hospital processes, providing security and efficiency in each one. However, there are scenarios where its application is especially strategic, as an identification failure would have direct and serious consequences for patient safety. At these critical points, biometrics isn’t just recommended, it’s essential.
Below, we explore three cases where implementing biometric identification offers an enormous value for safety within hospital processes.
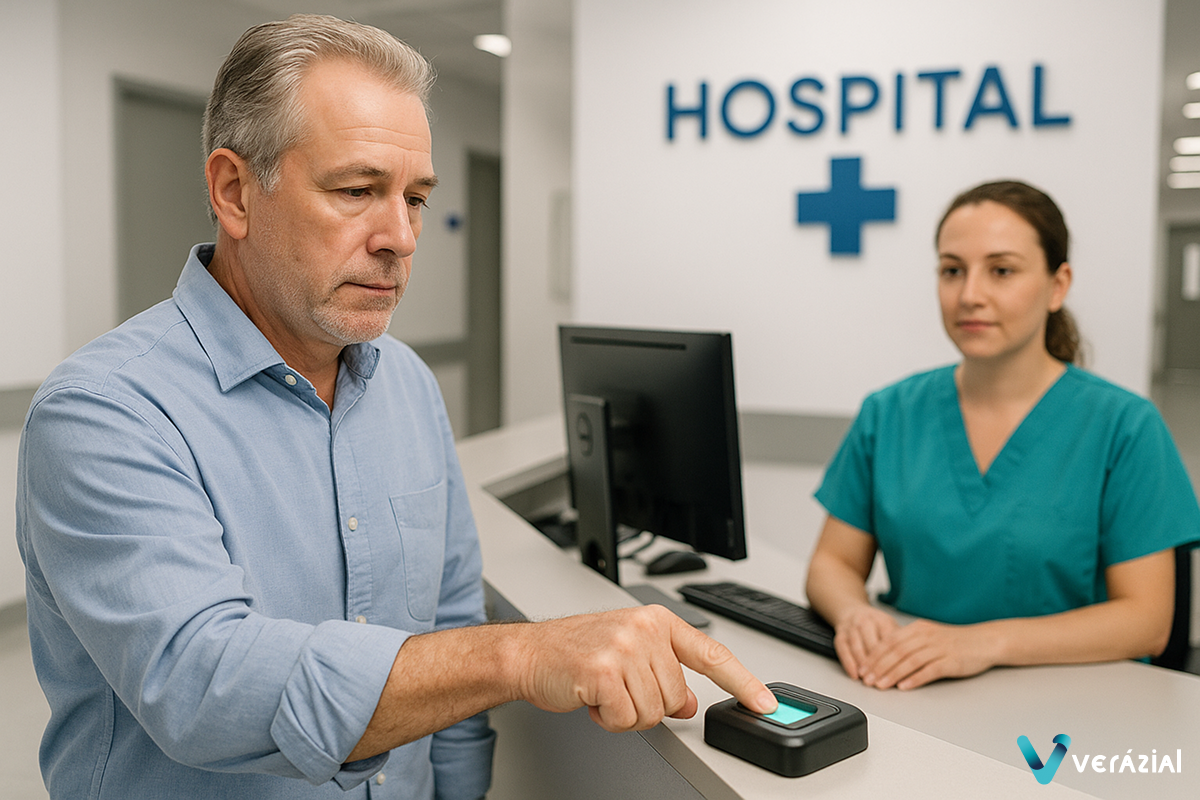
Admission: The First Step Toward Safe Care
Admission is the starting point of a patient’s hospital experience. At this stage, a registration error can lead to duplicate medical records, overlapping files, or even identity confusion, which subsequently results in incorrect diagnoses and treatments.
With biometrics, patients can be identified upon arrival at the hospital using their iris or fingerprint. This process ensures that their data is accurately linked to their clinical record, with no room for error. It also allows healthcare staff to confirm that the person being attended to is an exact match for the file they have on screen.
This initial step is critical because it lays the foundation for all subsequent care: if the admission information is correct, every doctor, nurse, or specialist will work with reliable and up-to-date data, eliminating risks from the very beginning.
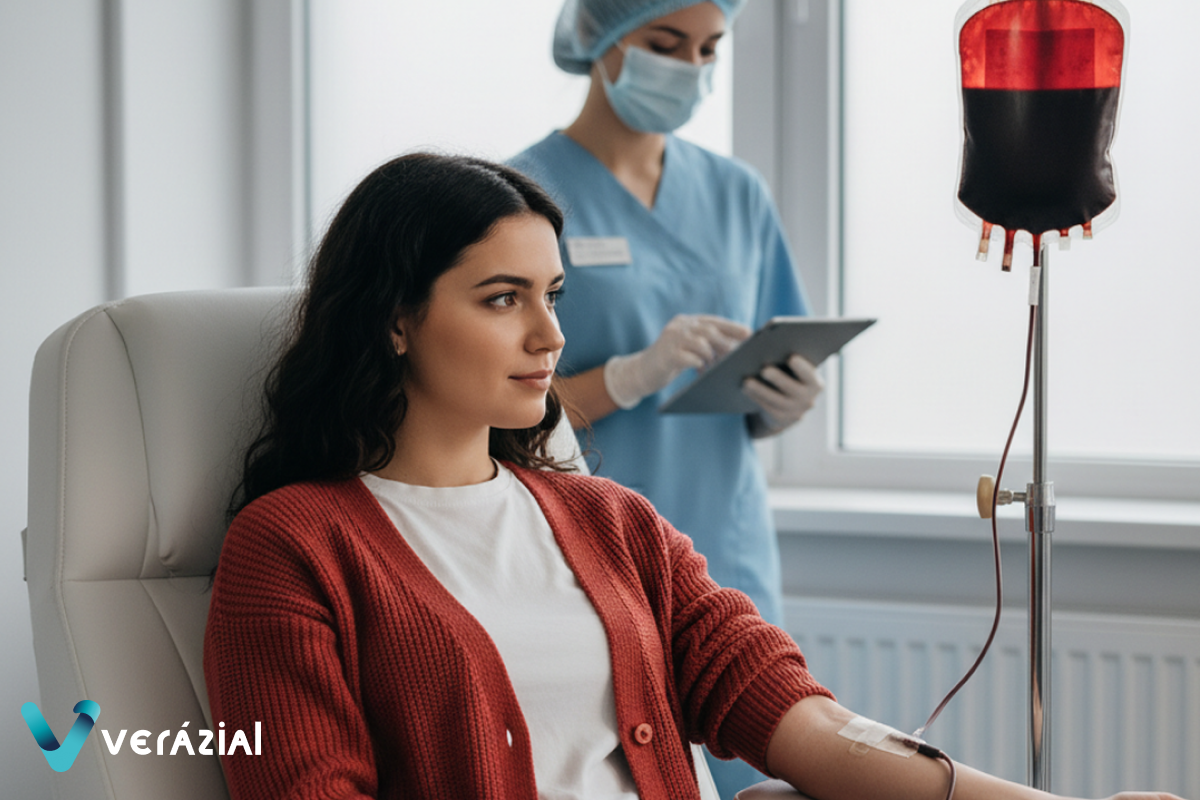
Blood Transfusions: Double Verification to Save Lives
Blood transfusions represent another critical point where an error can have fatal consequences. Administering a blood bag to the wrong patient or to a patient with an incompatible blood type can cause serious reactions and even death.
In this process, biometrics offer two-tiered verification. First, by identifying the patient before starting the procedure, ensuring that their medical history and prescription match the patient. Then, at the exact moment of administration, the nursing staff re-verifies the patient’s biometric identity, confirming that the blood bag they are about to administer is the correct one.
This double-check eliminates the risks from damaged wristbands, poorly printed labels, or simple human oversight, providing security that no traditional method can match.
Radiotherapy: Maximum Precision in High-Risk Treatments
Radiotherapy is one of the most sensitive treatments in hospital medicine. Radiation administration requires an absolute level of precision, as even the slightest mix-up in patient identification can result in the wrong dose being administered to the wrong person or in the wrong part of the body.
In this process, biometrics act as a security shield. Before entering the radiotherapy bunker, the patient is identified with biometric technology, which confirms without a margin of error that they are the person for whom the treatment is intended. Once their identity is validated, the oncologist and radiotherapist can proceed with the certainty that the therapy is being administered correctly.
The benefit isn’t just clinical. It also protects the medical team from liability due to unintentional errors and provides peace of mind to the patient, knowing they are receiving the exact treatment that was prescribed for them.

Advantages of Applying Biometrics at Critical Points
Implementing biometric technologies in hospitals provides multiple benefits that go beyond just error reduction:
- Reduction of adverse events: It eliminates errors resulting from physical identifiers or manual checks.
- Trust and peace of mind: Both patients and their families feel a greater sense of security in the care they receive.
- Regulatory compliance: It meets international recommendations for patient safety, aligning with quality standards and clinical audits.
- Operational efficiency: It reduces identification time and prevents duplicate records, which improves administrative management.
- Traceability and secure records: Each identification is documented in the system, offering transparency and support during internal or external reviews.
- Long-term cost reduction: While the initial investment may be significant, the savings derived from preventing errors, litigation, and additional hospitalizations far outweigh the costs.
We invite you to read our article “What benefits does biometric technology offer to hospitals and healthcare organizations?” to learn more about the benefits of implementing biometric technology for patient identification.
Precise Patient Identification Through Biometrics
Accurate patient identification is key to their safety. Biometrics is positioned as the most reliable option for critical processes such as admissions, transfusions, and radiotherapy. Its implementation protects lives, increases patient trust, and improves hospital efficiency, preparing institutions to meet higher demands and minimize identification errors.
Find out how Verázial ID solutions for hospitals can help you guarantee patient identification.
Contact us for a demonstration and/or a personalized study.
References
- Biologists wearing medical protective suits working in the microbiological hospital laboratory [Freepik]
Critical Patient Identification Points in Hospitals: The Value of Biometrics
Correct patient identification is essential for ensuring patient safety during medical care. In critical procedures such as admissions, blood transfusions, or radiotherapy, even a small error can have serious consequences. Implementing biometrics offers precise identification that protects the patient, reduces risks, and builds greater confidence throughout the entire care process.
In hospitals, patient safety largely depends on one fundamental factor: correct identification. Although it may seem like a simple process, an error in this step can have serious consequences, from misdiagnoses to wrong treatment being administered. According to The World Health Organization (WHO), millions of patients worldwide suffer harm each year due to medical errors, and a significant portion of these incidents are linked to identification errors.
Traditional methods, such as wristbands or manual checks, have been used for years, but they have limitations that make them vulnerable to human error, physical wear and tear, or even fraud. Faced with these risks, biometrics emerges as an advanced and reliable solution to ensure unequivocal identification during the highest-risk moments within a hospital. You can find more information about this in our article Patient identification in the healthcare environment.
What are the critical Patient Identification Points in Hospitals?
Patient identification should be present at all levels of care, but not all processes require the same level of rigor. There are critical points where any error can have irreversible consequences for the patient’s health and, consequently, for the reputation of the healthcare institution.
In these scenarios, biometrics provides a fundamental advantage: it ensures that each patient’s identity is unequivocally linked to their medical history, reducing the possibility of human error. By using technologies such as iris or fingerprint recognition, a level of precision is achieved that far surpasses traditional methods.
Biometrics can be integrated into multiple hospital processes, providing security and efficiency in each one. However, there are scenarios where its application is especially strategic, as an identification failure would have direct and serious consequences for patient safety. At these critical points, biometrics isn’t just recommended, it’s essential.
Below, we explore three cases where implementing biometric identification offers an enormous value for safety within hospital processes.
Admission: The First Step Toward Safe Care
Admission is the starting point of a patient’s hospital experience. At this stage, a registration error can lead to duplicate medical records, overlapping files, or even identity confusion, which subsequently results in incorrect diagnoses and treatments.
With biometrics, patients can be identified upon arrival at the hospital using their iris or fingerprint. This process ensures that their data is accurately linked to their clinical record, with no room for error. It also allows healthcare staff to confirm that the person being attended to is an exact match for the file they have on screen.
This initial step is critical because it lays the foundation for all subsequent care: if the admission information is correct, every doctor, nurse, or specialist will work with reliable and up-to-date data, eliminating risks from the very beginning.
Blood Transfusions: Double Verification to Save Lives
Blood transfusions represent another critical point where an error can have fatal consequences. Administering a blood bag to the wrong patient or to a patient with an incompatible blood type can cause serious reactions and even death.
In this process, biometrics offer two-tiered verification. First, by identifying the patient before starting the procedure, ensuring that their medical history and prescription match the patient. Then, at the exact moment of administration, the nursing staff re-verifies the patient’s biometric identity, confirming that the blood bag they are about to administer is the correct one.
This double-check eliminates the risks from damaged wristbands, poorly printed labels, or simple human oversight, providing security that no traditional method can match.
Radiotherapy: Maximum Precision in High-Risk Treatments
Radiotherapy is one of the most sensitive treatments in hospital medicine. Radiation administration requires an absolute level of precision, as even the slightest mix-up in patient identification can result in the wrong dose being administered to the wrong person or in the wrong part of the body.
In this process, biometrics act as a security shield. Before entering the radiotherapy bunker, the patient is identified with biometric technology, which confirms without a margin of error that they are the person for whom the treatment is intended. Once their identity is validated, the oncologist and radiotherapist can proceed with the certainty that the therapy is being administered correctly.
The benefit isn’t just clinical. It also protects the medical team from liability due to unintentional errors and provides peace of mind to the patient, knowing they are receiving the exact treatment that was prescribed for them.

Advantages of Applying Biometrics at Critical Points
Implementing biometric technologies in hospitals provides multiple benefits that go beyond just error reduction:
- Reduction of adverse events: It eliminates errors resulting from physical identifiers or manual checks.
- Trust and peace of mind: Both patients and their families feel a greater sense of security in the care they receive.
- Regulatory compliance: It meets international recommendations for patient safety, aligning with quality standards and clinical audits.
- Operational efficiency: It reduces identification time and prevents duplicate records, which improves administrative management.
- Traceability and secure records: Each identification is documented in the system, offering transparency and support during internal or external reviews.
- Long-term cost reduction: While the initial investment may be significant, the savings derived from preventing errors, litigation, and additional hospitalizations far outweigh the costs.
We invite you to read our article “What benefits does biometric technology offer to hospitals and healthcare organizations?” to learn more about the benefits of implementing biometric technology for patient identification.
Precise Patient Identification Through Biometrics
Accurate patient identification is key to their safety. Biometrics is positioned as the most reliable option for critical processes such as admissions, transfusions, and radiotherapy. Its implementation protects lives, increases patient trust, and improves hospital efficiency, preparing institutions to meet higher demands and minimize identification errors.
Find out how Verázial ID solutions for hospitals can help you guarantee patient identification.
Contact us for a demonstration and/or a personalized study.
References
- Biologists wearing medical protective suits working in the microbiological hospital laboratory [Freepik]
Critical Patient Identification Points in Hospitals: The Value of Biometrics
Correct patient identification is essential for ensuring patient safety during medical care. In critical procedures such as admissions, blood transfusions, or radiotherapy, even a small error can have serious consequences. Implementing biometrics offers precise identification that protects the patient, reduces risks, and builds greater confidence throughout the entire care process.
In hospitals, patient safety largely depends on one fundamental factor: correct identification. Although it may seem like a simple process, an error in this step can have serious consequences, from misdiagnoses to wrong treatment being administered. According to The World Health Organization (WHO), millions of patients worldwide suffer harm each year due to medical errors, and a significant portion of these incidents are linked to identification errors.
Traditional methods, such as wristbands or manual checks, have been used for years, but they have limitations that make them vulnerable to human error, physical wear and tear, or even fraud. Faced with these risks, biometrics emerges as an advanced and reliable solution to ensure unequivocal identification during the highest-risk moments within a hospital. You can find more information about this in our article Patient identification in the healthcare environment.
What are the critical Patient Identification Points in Hospitals?
Patient identification should be present at all levels of care, but not all processes require the same level of rigor. There are critical points where any error can have irreversible consequences for the patient’s health and, consequently, for the reputation of the healthcare institution.
In these scenarios, biometrics provides a fundamental advantage: it ensures that each patient’s identity is unequivocally linked to their medical history, reducing the possibility of human error. By using technologies such as iris or fingerprint recognition, a level of precision is achieved that far surpasses traditional methods.
Biometrics can be integrated into multiple hospital processes, providing security and efficiency in each one. However, there are scenarios where its application is especially strategic, as an identification failure would have direct and serious consequences for patient safety. At these critical points, biometrics isn’t just recommended, it’s essential.
Below, we explore three cases where implementing biometric identification offers an enormous value for safety within hospital processes.
Admission: The First Step Toward Safe Care
Admission is the starting point of a patient’s hospital experience. At this stage, a registration error can lead to duplicate medical records, overlapping files, or even identity confusion, which subsequently results in incorrect diagnoses and treatments.
With biometrics, patients can be identified upon arrival at the hospital using their iris or fingerprint. This process ensures that their data is accurately linked to their clinical record, with no room for error. It also allows healthcare staff to confirm that the person being attended to is an exact match for the file they have on screen.
This initial step is critical because it lays the foundation for all subsequent care: if the admission information is correct, every doctor, nurse, or specialist will work with reliable and up-to-date data, eliminating risks from the very beginning.
Blood Transfusions: Double Verification to Save Lives
Blood transfusions represent another critical point where an error can have fatal consequences. Administering a blood bag to the wrong patient or to a patient with an incompatible blood type can cause serious reactions and even death.
In this process, biometrics offer two-tiered verification. First, by identifying the patient before starting the procedure, ensuring that their medical history and prescription match the patient. Then, at the exact moment of administration, the nursing staff re-verifies the patient’s biometric identity, confirming that the blood bag they are about to administer is the correct one.
This double-check eliminates the risks from damaged wristbands, poorly printed labels, or simple human oversight, providing security that no traditional method can match.
Radiotherapy: Maximum Precision in High-Risk Treatments
Radiotherapy is one of the most sensitive treatments in hospital medicine. Radiation administration requires an absolute level of precision, as even the slightest mix-up in patient identification can result in the wrong dose being administered to the wrong person or in the wrong part of the body.
In this process, biometrics act as a security shield. Before entering the radiotherapy bunker, the patient is identified with biometric technology, which confirms without a margin of error that they are the person for whom the treatment is intended. Once their identity is validated, the oncologist and radiotherapist can proceed with the certainty that the therapy is being administered correctly.
The benefit isn’t just clinical. It also protects the medical team from liability due to unintentional errors and provides peace of mind to the patient, knowing they are receiving the exact treatment that was prescribed for them.

Advantages of Applying Biometrics at Critical Points
Implementing biometric technologies in hospitals provides multiple benefits that go beyond just error reduction:
- Reduction of adverse events: It eliminates errors resulting from physical identifiers or manual checks.
- Trust and peace of mind: Both patients and their families feel a greater sense of security in the care they receive.
- Regulatory compliance: It meets international recommendations for patient safety, aligning with quality standards and clinical audits.
- Operational efficiency: It reduces identification time and prevents duplicate records, which improves administrative management.
- Traceability and secure records: Each identification is documented in the system, offering transparency and support during internal or external reviews.
- Long-term cost reduction: While the initial investment may be significant, the savings derived from preventing errors, litigation, and additional hospitalizations far outweigh the costs.
We invite you to read our article “What benefits does biometric technology offer to hospitals and healthcare organizations?” to learn more about the benefits of implementing biometric technology for patient identification.
Precise Patient Identification Through Biometrics
Accurate patient identification is key to their safety. Biometrics is positioned as the most reliable option for critical processes such as admissions, transfusions, and radiotherapy. Its implementation protects lives, increases patient trust, and improves hospital efficiency, preparing institutions to meet higher demands and minimize identification errors.
Find out how Verázial ID solutions for hospitals can help you guarantee patient identification.
Contact us for a demonstration and/or a personalized study.
References
- Biologists wearing medical protective suits working in the microbiological hospital laboratory [Freepik]
You May Also Like
You May Also Like