How to Ensure Safety in Radiotherapy Treatments Through Biometric Identification?
Biometric identification in radiotherapy strengthens safety at every stage of the treatment process, ensuring each dose is delivered to the right patient. This prevents serious clinical errors, protects access to critical areas, and guarantees complete traceability, safeguarding patient health and maintaining the quality of the procedure.
Ensuring patient safety is a core principle of healthcare. Every procedure, every treatment, and every clinical interaction must prioritize protecting the health and integrity of the person receiving care. Despite advancements in safety protocols, digitalization, and staff training, preventable medical errors remain a persistent challenge in hospitals worldwide.
One of the most critical mistakes that can occur in a hospital setting is the incorrect identification of a patient, a failure that can trigger serious consequences: administering the wrong treatment, performing invasive procedures on the wrong person, or allowing unauthorized access to critical hospital areas. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes accurate patient identification as one of the top priorities for preventing significant harm.
Although many hospitals rely on traditional methods such as barcode wristbands, photographs, double-check forms, or verbal identification, these approaches have limitations. They can fail due to wear and tear, human error, or tampering—leaving room for critical incidents, especially in highly invasive treatments like radiotherapy.
Can Errors Occur in Radiotherapy?
While radiotherapy is widely regarded as one of the safest areas in medicine, no procedure is entirely risk-free. This treatment is highly personalized and follows a protocol that can involve up to ten steps: patient assessment, decision to treat, protocol prescription, positioning and immobilization, simulation and imaging for volume determination, treatment planning, transfer of treatment information, patient setup, treatment delivery, and post-treatment verification and follow-up.
An error in patient identification at any of these stages, particularly during treatment delivery, can have severe consequences, including unnecessary radiation exposure or missing the required treatment altogether.
In most hospitals, patient identification in radiotherapy relies on verbal confirmation and document checks: the patient states their name, shows identification, and the staff compares it with the treatment schedule. However, this system has certain vulnerabilities:
- Confusion at reception: Selecting the wrong patient in the software or assigning them incorrectly on the waiting list.
- Similar names: Patients with similar personal data being sent to the wrong treatment room.
- Unrecorded movements: Temporary departures without notification, causing uncertainty about a patient’s actual presence.
- Errors at the linear accelerator: Calling or selecting another person’s record during treatment delivery.
Although these may seem like administrative slip-ups, their consequences are clinical and potentially serious. Radiotherapy is highly personalized and delivering radiation to the wrong person can cause irreversible harm or even endanger a patient’s life.
Consequences of Incorrect Identification
Misidentification in radiotherapy can have both immediate and long-term effects on patient safety and treatment quality.
- Radiation delivered to the wrong patient: Each radiotherapy session is precisely tailored to the type of tumor, prescribed dose, and patient anatomy. A mix-up can result in radiation being delivered to someone else, damaging healthy tissue unnecessarily while leaving the actual tumor untreated.
- Treatment record errors: Incorrect identification can result in the patient’s medical record containing information belonging to another person, compromising traceability and treatment follow-up.
- Incorrect dosage risk: Confusion between patients can lead to overdosing or underdosing, reducing treatment effectiveness and increasing the likelihood of adverse effects.
- Treatment delays and interruptions: A misidentified patient may take another’s appointment slot or be sent to the wrong treatment bunker, delaying their own therapy and disrupting scheduling for others.
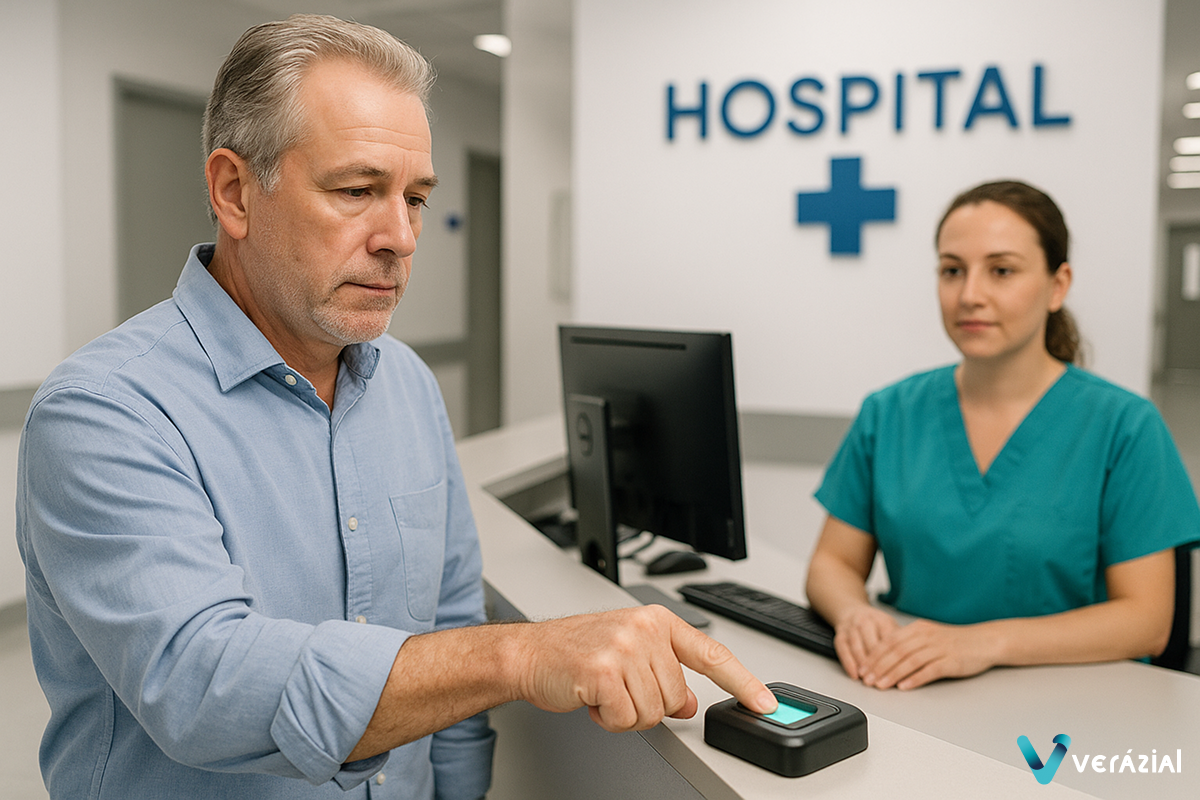
Biometrics: A Secure Solution for Patient Identification
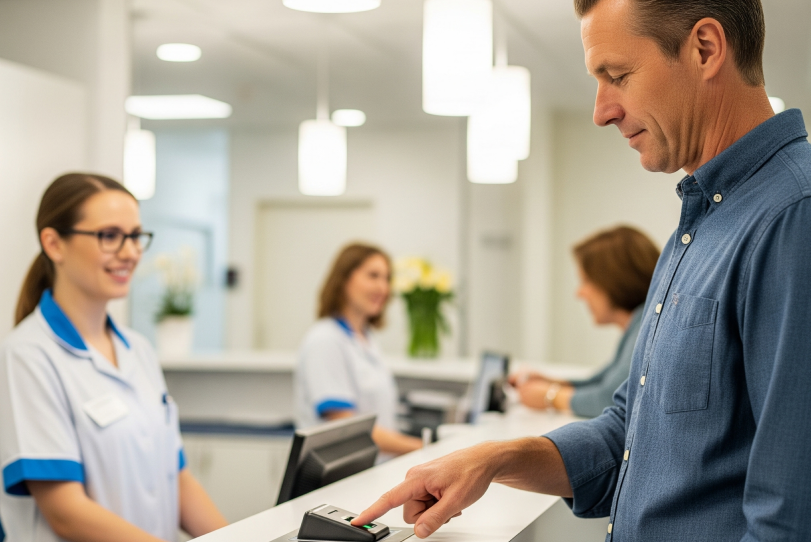

To ensure accurate patient identification across all clinical procedures, the most effective solution is implementing biometric technologies, delivering precision, reliability, and security in identity verification.
Biometrics, based on unique and non-transferable physical traits such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial recognition, represents a significant advancement over traditional methods. It allows for unequivocal patient identification, even in critical situations or when the patient is unable to communicate.
When implemented in radiotherapy and other hospital settings, biometrics offers multiple benefits:
- Prevents clinical errors: Ensures each patient receives the correct treatment, avoiding accidental administration of therapies intended for someone else.
- Eliminates confusion among patients with similar names: Biometric precision removes dependence on verbal checks or manual documentation.
- Protects against identity fraud: Reduces legal risks and ensures proper use of hospital resources.
- Accurate linkage to medical records: Every treatment, test, and procedure is correctly linked to the right patient, improving care quality.
- Streamlines clinical and administrative processes: Automation reduces staff workload and provides real-time traceability.
Beyond patient identification, biometrics can also be integrated into access control systems for sensitive areas, ensuring only authorized personnel enter operating rooms, radiotherapy bunkers, or critical care units—enhancing overall hospital security.
Biometrics is not just a technological innovation, it’s a decisive step toward excellence in patient care.
Recommended reading for further insight:
Find out how Verázial ID Health can help you ensure secure patient identification.
Contact us for a demonstration and/or a tailored assessment.
References
- Doctor preparing the patient for the CT scan.[Freepik]
How to Ensure Safety in Radiotherapy Treatments Through Biometric Identification?
Biometric identification in radiotherapy strengthens safety at every stage of the treatment process, ensuring each dose is delivered to the right patient. This prevents serious clinical errors, protects access to critical areas, and guarantees complete traceability, safeguarding patient health and maintaining the quality of the procedure.
Ensuring patient safety is a core principle of healthcare. Every procedure, every treatment, and every clinical interaction must prioritize protecting the health and integrity of the person receiving care. Despite advancements in safety protocols, digitalization, and staff training, preventable medical errors remain a persistent challenge in hospitals worldwide.
One of the most critical mistakes that can occur in a hospital setting is the incorrect identification of a patient, a failure that can trigger serious consequences: administering the wrong treatment, performing invasive procedures on the wrong person, or allowing unauthorized access to critical hospital areas. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes accurate patient identification as one of the top priorities for preventing significant harm.
Although many hospitals rely on traditional methods such as barcode wristbands, photographs, double-check forms, or verbal identification, these approaches have limitations. They can fail due to wear and tear, human error, or tampering—leaving room for critical incidents, especially in highly invasive treatments like radiotherapy.
Can Errors Occur in Radiotherapy?
While radiotherapy is widely regarded as one of the safest areas in medicine, no procedure is entirely risk-free. This treatment is highly personalized and follows a protocol that can involve up to ten steps: patient assessment, decision to treat, protocol prescription, positioning and immobilization, simulation and imaging for volume determination, treatment planning, transfer of treatment information, patient setup, treatment delivery, and post-treatment verification and follow-up.
An error in patient identification at any of these stages, particularly during treatment delivery, can have severe consequences, including unnecessary radiation exposure or missing the required treatment altogether.
In most hospitals, patient identification in radiotherapy relies on verbal confirmation and document checks: the patient states their name, shows identification, and the staff compares it with the treatment schedule. However, this system has certain vulnerabilities:
- Confusion at reception: Selecting the wrong patient in the software or assigning them incorrectly on the waiting list.
- Similar names: Patients with similar personal data being sent to the wrong treatment room.
- Unrecorded movements: Temporary departures without notification, causing uncertainty about a patient’s actual presence.
- Errors at the linear accelerator: Calling or selecting another person’s record during treatment delivery.
Although these may seem like administrative slip-ups, their consequences are clinical and potentially serious. Radiotherapy is highly personalized and delivering radiation to the wrong person can cause irreversible harm or even endanger a patient’s life.
Consequences of Incorrect Identification
Misidentification in radiotherapy can have both immediate and long-term effects on patient safety and treatment quality.
- Radiation delivered to the wrong patient: Each radiotherapy session is precisely tailored to the type of tumor, prescribed dose, and patient anatomy. A mix-up can result in radiation being delivered to someone else, damaging healthy tissue unnecessarily while leaving the actual tumor untreated.
- Treatment record errors: Incorrect identification can result in the patient’s medical record containing information belonging to another person, compromising traceability and treatment follow-up.
- Incorrect dosage risk: Confusion between patients can lead to overdosing or underdosing, reducing treatment effectiveness and increasing the likelihood of adverse effects.
- Treatment delays and interruptions: A misidentified patient may take another’s appointment slot or be sent to the wrong treatment bunker, delaying their own therapy and disrupting scheduling for others.
Biometrics: A Secure Solution for Patient Identification

To ensure accurate patient identification across all clinical procedures, the most effective solution is implementing biometric technologies, delivering precision, reliability, and security in identity verification.
Biometrics, based on unique and non-transferable physical traits such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial recognition, represents a significant advancement over traditional methods. It allows for unequivocal patient identification, even in critical situations or when the patient is unable to communicate.
When implemented in radiotherapy and other hospital settings, biometrics offers multiple benefits:
- Prevents clinical errors: Ensures each patient receives the correct treatment, avoiding accidental administration of therapies intended for someone else.
- Eliminates confusion among patients with similar names: Biometric precision removes dependence on verbal checks or manual documentation.
- Protects against identity fraud: Reduces legal risks and ensures proper use of hospital resources.
- Accurate linkage to medical records: Every treatment, test, and procedure is correctly linked to the right patient, improving care quality.
- Streamlines clinical and administrative processes: Automation reduces staff workload and provides real-time traceability.
Beyond patient identification, biometrics can also be integrated into access control systems for sensitive areas, ensuring only authorized personnel enter operating rooms, radiotherapy bunkers, or critical care units—enhancing overall hospital security.
Biometrics is not just a technological innovation, it’s a decisive step toward excellence in patient care.
Recommended reading for further insight:
Find out how Verázial ID Health can help you ensure secure patient identification.
Contact us for a demonstration and/or a tailored assessment.
References
- Doctor preparing the patient for the CT scan.[Freepik]
How to Ensure Safety in Radiotherapy Treatments Through Biometric Identification?
Biometric identification in radiotherapy strengthens safety at every stage of the treatment process, ensuring each dose is delivered to the right patient. This prevents serious clinical errors, protects access to critical areas, and guarantees complete traceability, safeguarding patient health and maintaining the quality of the procedure.
Ensuring patient safety is a core principle of healthcare. Every procedure, every treatment, and every clinical interaction must prioritize protecting the health and integrity of the person receiving care. Despite advancements in safety protocols, digitalization, and staff training, preventable medical errors remain a persistent challenge in hospitals worldwide.
One of the most critical mistakes that can occur in a hospital setting is the incorrect identification of a patient, a failure that can trigger serious consequences: administering the wrong treatment, performing invasive procedures on the wrong person, or allowing unauthorized access to critical hospital areas. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes accurate patient identification as one of the top priorities for preventing significant harm.
Although many hospitals rely on traditional methods such as barcode wristbands, photographs, double-check forms, or verbal identification, these approaches have limitations. They can fail due to wear and tear, human error, or tampering—leaving room for critical incidents, especially in highly invasive treatments like radiotherapy.
Can Errors Occur in Radiotherapy?
While radiotherapy is widely regarded as one of the safest areas in medicine, no procedure is entirely risk-free. This treatment is highly personalized and follows a protocol that can involve up to ten steps: patient assessment, decision to treat, protocol prescription, positioning and immobilization, simulation and imaging for volume determination, treatment planning, transfer of treatment information, patient setup, treatment delivery, and post-treatment verification and follow-up.
An error in patient identification at any of these stages, particularly during treatment delivery, can have severe consequences, including unnecessary radiation exposure or missing the required treatment altogether.
In most hospitals, patient identification in radiotherapy relies on verbal confirmation and document checks: the patient states their name, shows identification, and the staff compares it with the treatment schedule. However, this system has certain vulnerabilities:
- Confusion at reception: Selecting the wrong patient in the software or assigning them incorrectly on the waiting list.
- Similar names: Patients with similar personal data being sent to the wrong treatment room.
- Unrecorded movements: Temporary departures without notification, causing uncertainty about a patient’s actual presence.
- Errors at the linear accelerator: Calling or selecting another person’s record during treatment delivery.
Although these may seem like administrative slip-ups, their consequences are clinical and potentially serious. Radiotherapy is highly personalized and delivering radiation to the wrong person can cause irreversible harm or even endanger a patient’s life.
Consequences of Incorrect Identification
Misidentification in radiotherapy can have both immediate and long-term effects on patient safety and treatment quality.
- Radiation delivered to the wrong patient: Each radiotherapy session is precisely tailored to the type of tumor, prescribed dose, and patient anatomy. A mix-up can result in radiation being delivered to someone else, damaging healthy tissue unnecessarily while leaving the actual tumor untreated.
- Treatment record errors: Incorrect identification can result in the patient’s medical record containing information belonging to another person, compromising traceability and treatment follow-up.
- Incorrect dosage risk: Confusion between patients can lead to overdosing or underdosing, reducing treatment effectiveness and increasing the likelihood of adverse effects.
- Treatment delays and interruptions: A misidentified patient may take another’s appointment slot or be sent to the wrong treatment bunker, delaying their own therapy and disrupting scheduling for others.
Biometrics: A Secure Solution for Patient Identification

To ensure accurate patient identification across all clinical procedures, the most effective solution is implementing biometric technologies, delivering precision, reliability, and security in identity verification.
Biometrics, based on unique and non-transferable physical traits such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial recognition, represents a significant advancement over traditional methods. It allows for unequivocal patient identification, even in critical situations or when the patient is unable to communicate.
When implemented in radiotherapy and other hospital settings, biometrics offers multiple benefits:
- Prevents clinical errors: Ensures each patient receives the correct treatment, avoiding accidental administration of therapies intended for someone else.
- Eliminates confusion among patients with similar names: Biometric precision removes dependence on verbal checks or manual documentation.
- Protects against identity fraud: Reduces legal risks and ensures proper use of hospital resources.
- Accurate linkage to medical records: Every treatment, test, and procedure is correctly linked to the right patient, improving care quality.
- Streamlines clinical and administrative processes: Automation reduces staff workload and provides real-time traceability.
Beyond patient identification, biometrics can also be integrated into access control systems for sensitive areas, ensuring only authorized personnel enter operating rooms, radiotherapy bunkers, or critical care units—enhancing overall hospital security.
Biometrics is not just a technological innovation, it’s a decisive step toward excellence in patient care.
Recommended reading for further insight:
Find out how Verázial ID Health can help you ensure secure patient identification.
Contact us for a demonstration and/or a tailored assessment.
References
- Doctor preparing the patient for the CT scan.[Freepik]
You May Also Like
You May Also Like