Use of biometric technology in criminal investigations
Accuracy in identifying suspects and analyzing evidence is crucial to avoid errors in criminal investigations. The implementation of biometric technologies, such as fingerprint, facial and iris recognition, allows for fast and reliable identification, improving the authenticity of evidence and strengthening trust in the judicial system.
Criminal investigation, also known as Criminalistics, is the science that allows the study and analysis of criminal acts through scientific methods and techniques. It focuses on the collection, recognition, examination and interpretation of physical evidence, such as fingerprints, traces and other residue, in order to scientifically demonstrate the relationship between the evidence and the crime.
In Criminalistics, forensic science technicians play a fundamental role, as they are in charge of collecting and analyzing physical evidence both at the crime scene and in specialized laboratories. Their work is not only critical in identifying the possible perpetrators of a crime, but also in providing scientific and irrefutable evidence in court trials.
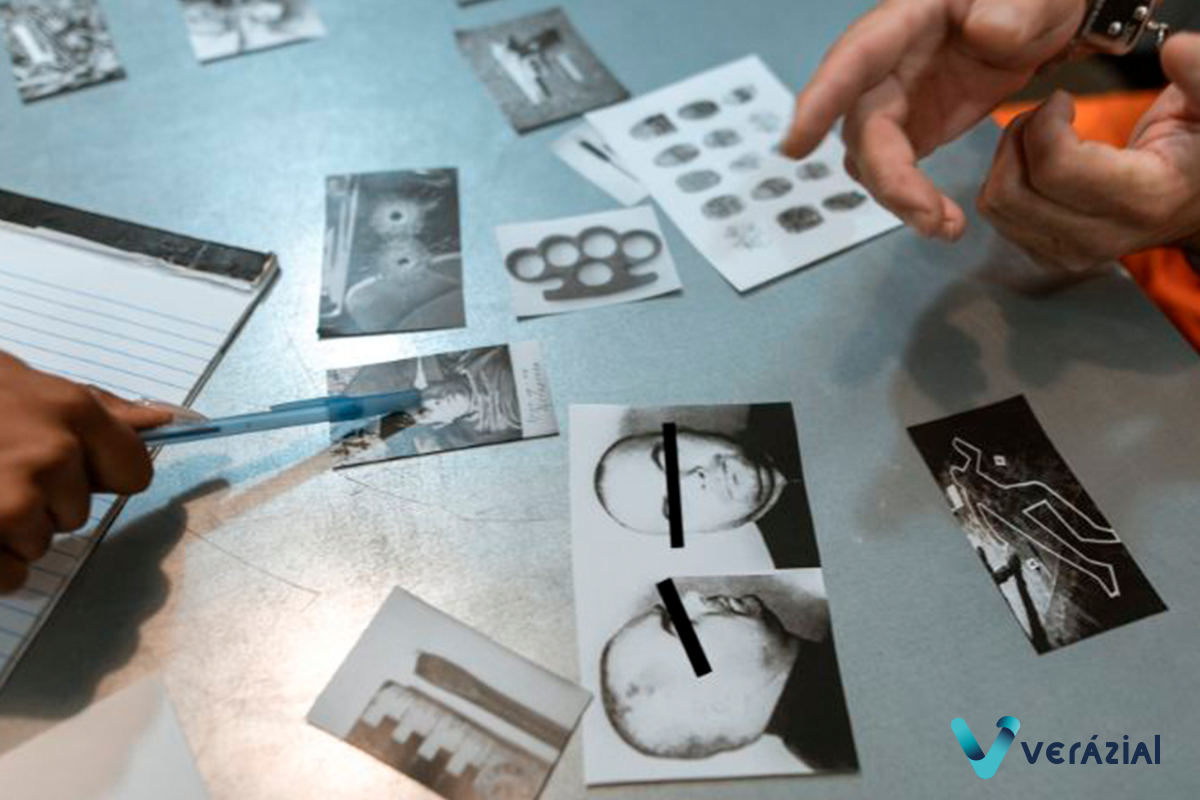
At a crime scene, various types of evidence, both biometric and non-biometric, can be collected, which help to identify the individuals involved and map out the lines of investigation. The most common biometric samples taken are fingerprints, palm prints, DNA samples, facial images and voice patterns. Each of these pieces of evidence allows for accurate identifications, which are critical to building a solid case.
In many cases, the collected prints may be latent and partial, especially when it comes to fingerprints and palm prints. Latent prints are those that are not visible to the naked eye and require special techniques to be detected. This type of evidence requires careful analysis as it can be fragmentary and may correspond to one or more individuals.
Technicians must carry out detailed “one-to-one” comparisons to determine possible matches, which can be challenging when there is uncertainty about the number of people present at the scene. Proper collection and preservation of these samples are crucial in ensuring that the evidence remains valid and can be admitted in legal proceedings.
The importance of accuracy in evidence processing
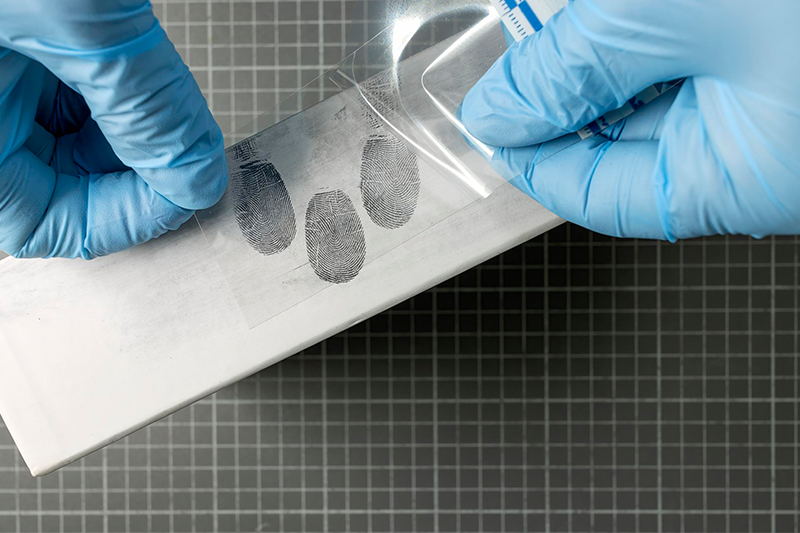

Accurate identification and processing of evidence is essential to maintain the integrity of the judicial system. In criminal investigations, one of the most relevant types of evidence are biometric samples, especially fingerprints, which can be collected both at crime scenes and at forensic anatomical institutes to identify suspects or perform post-mortem identifications. Inaccurate collection or analysis of these samples can lead to serious miscarriages of justice, from the wrongful indictment of innocent people to the exoneration of the guilty, affecting both the victims and the credibility of the system.
Moreover, diligence is key in the analysis of evidence, in order for it to be considered irrefutable in trials. Lack of precision can make it difficult to link suspects to crime scenes due to insufficient evidence or issues with correctly identifying faces in images or videos. This risk also impacts the identification of deceased individuals or living persons through fingerprints, as insecure or slow methods can delay the investigation and hinder the effective resolution of cases. Accuracy not only facilitates the precise identification of individuals, but also strengthens public confidence in judicial proceedings and optimizes investigative resources.
The use of biometrics and its role in criminal investigation
Biometrics has profoundly transformed the approach to criminal investigations, providing advanced and accurate methods for suspect identification and evidence authentication. The ability to identify unique and unalterable characteristics of individuals, such as fingerprints, iris patterns or facial features, has greatly improved the accuracy of investigative processes. This technology streamlines procedures, optimizes the use of resources and reinforces the credibility of the judicial system by ensuring the authenticity of the evidence.
Today’s biometric software is specifically designed to assist forensic scientists in the collection and analysis of evidence in criminal investigations, offering multiple key applications:
- Identification of suspects and criminals: Through latent fingerprints and palm prints collected from various objects, these systems enable the fast and secure identification of individuals, even when the evidence is partial or fragmented.
- Identification of corpses: In forensic anatomy institutes and crime scenes, the software allows for quick and secure identification of bodies through fingerprints and palm prints, speeding up a critical process in investigations.
- Facial recognition from images or videos: In cases where there are photos or videos of suspects, facial biometrics provides an accurate and reliable means of identification, essential in scenarios where there are no physical prints.
- Identity verification of living individuals: By using fingerprints, iris and facial recognition, the software allows unequivocal verification of living individuals’ identity, even when there are doubts about their true identity, ensuring the authenticity of the identification in real time.
- Criminal case management: The software organizes and stores collected fingerprints, photos and videos, enabling efficient case management and ensuring that all evidence is available for analysis and eventual presentation at trial.
- Real-time interconnection: The technology allows real-time connections with other biometric databases (Civil Registry, Electoral Court, Prisons, Police, etc.), expanding the identification range and facilitating the pursuit for suspects through a more extensive search.
- International collaboration: Systems can exchange biometric data with international security agencies in appropriate formats and standards, contributing to the global fight against crime.
Discover Verázial ID Criminalistics our solution designed to ensure that every piece of evidence and every piece of data collected in criminal investigations can be used reliably.
Contact us for a demo and/or personalized assessment.
Use of biometric technology in criminal investigations
Accuracy in identifying suspects and analyzing evidence is crucial to avoid errors in criminal investigations. The implementation of biometric technologies, such as fingerprint, facial and iris recognition, allows for fast and reliable identification, improving the authenticity of evidence and strengthening trust in the judicial system.
Criminal investigation, also known as Criminalistics, is the science that allows the study and analysis of criminal acts through scientific methods and techniques. It focuses on the collection, recognition, examination and interpretation of physical evidence, such as fingerprints, traces and other residue, in order to scientifically demonstrate the relationship between the evidence and the crime.
In Criminalistics, forensic science technicians play a fundamental role, as they are in charge of collecting and analyzing physical evidence both at the crime scene and in specialized laboratories. Their work is not only critical in identifying the possible perpetrators of a crime, but also in providing scientific and irrefutable evidence in court trials.
At a crime scene, various types of evidence, both biometric and non-biometric, can be collected, which help to identify the individuals involved and map out the lines of investigation. The most common biometric samples taken are fingerprints, palm prints, DNA samples, facial images and voice patterns. Each of these pieces of evidence allows for accurate identifications, which are critical to building a solid case.
In many cases, the collected prints may be latent and partial, especially when it comes to fingerprints and palm prints. Latent prints are those that are not visible to the naked eye and require special techniques to be detected. This type of evidence requires careful analysis as it can be fragmentary and may correspond to one or more individuals.
Technicians must carry out detailed “one-to-one” comparisons to determine possible matches, which can be challenging when there is uncertainty about the number of people present at the scene. Proper collection and preservation of these samples are crucial in ensuring that the evidence remains valid and can be admitted in legal proceedings.
The importance of accuracy in evidence processing

Accurate identification and processing of evidence is essential to maintain the integrity of the judicial system. In criminal investigations, one of the most relevant types of evidence are biometric samples, especially fingerprints, which can be collected both at crime scenes and at forensic anatomical institutes to identify suspects or perform post-mortem identifications. Inaccurate collection or analysis of these samples can lead to serious miscarriages of justice, from the wrongful indictment of innocent people to the exoneration of the guilty, affecting both the victims and the credibility of the system.
Moreover, diligence is key in the analysis of evidence, in order for it to be considered irrefutable in trials. Lack of precision can make it difficult to link suspects to crime scenes due to insufficient evidence or issues with correctly identifying faces in images or videos. This risk also impacts the identification of deceased individuals or living persons through fingerprints, as insecure or slow methods can delay the investigation and hinder the effective resolution of cases. Accuracy not only facilitates the precise identification of individuals, but also strengthens public confidence in judicial proceedings and optimizes investigative resources.
The use of biometrics and its role in criminal investigation
Biometrics has profoundly transformed the approach to criminal investigations, providing advanced and accurate methods for suspect identification and evidence authentication. The ability to identify unique and unalterable characteristics of individuals, such as fingerprints, iris patterns or facial features, has greatly improved the accuracy of investigative processes. This technology streamlines procedures, optimizes the use of resources and reinforces the credibility of the judicial system by ensuring the authenticity of the evidence.
Today’s biometric software is specifically designed to assist forensic scientists in the collection and analysis of evidence in criminal investigations, offering multiple key applications:
- Identification of suspects and criminals: Through latent fingerprints and palm prints collected from various objects, these systems enable the fast and secure identification of individuals, even when the evidence is partial or fragmented.
- Identification of corpses: In forensic anatomy institutes and crime scenes, the software allows for quick and secure identification of bodies through fingerprints and palm prints, speeding up a critical process in investigations.
- Facial recognition from images or videos: In cases where there are photos or videos of suspects, facial biometrics provides an accurate and reliable means of identification, essential in scenarios where there are no physical prints.
- Identity verification of living individuals: By using fingerprints, iris and facial recognition, the software allows unequivocal verification of living individuals’ identity, even when there are doubts about their true identity, ensuring the authenticity of the identification in real time.
- Criminal case management: The software organizes and stores collected fingerprints, photos and videos, enabling efficient case management and ensuring that all evidence is available for analysis and eventual presentation at trial.
- Real-time interconnection: The technology allows real-time connections with other biometric databases (Civil Registry, Electoral Court, Prisons, Police, etc.), expanding the identification range and facilitating the pursuit for suspects through a more extensive search.
- International collaboration: Systems can exchange biometric data with international security agencies in appropriate formats and standards, contributing to the global fight against crime.
Discover Verázial ID Criminalistics our solution designed to ensure that every piece of evidence and every piece of data collected in criminal investigations can be used reliably.
Contact us for a demo and/or personalized assessment.
Use of biometric technology in criminal investigations
Accuracy in identifying suspects and analyzing evidence is crucial to avoid errors in criminal investigations. The implementation of biometric technologies, such as fingerprint, facial and iris recognition, allows for fast and reliable identification, improving the authenticity of evidence and strengthening trust in the judicial system.
Criminal investigation, also known as Criminalistics, is the science that allows the study and analysis of criminal acts through scientific methods and techniques. It focuses on the collection, recognition, examination and interpretation of physical evidence, such as fingerprints, traces and other residue, in order to scientifically demonstrate the relationship between the evidence and the crime.
In Criminalistics, forensic science technicians play a fundamental role, as they are in charge of collecting and analyzing physical evidence both at the crime scene and in specialized laboratories. Their work is not only critical in identifying the possible perpetrators of a crime, but also in providing scientific and irrefutable evidence in court trials.
At a crime scene, various types of evidence, both biometric and non-biometric, can be collected, which help to identify the individuals involved and map out the lines of investigation. The most common biometric samples taken are fingerprints, palm prints, DNA samples, facial images and voice patterns. Each of these pieces of evidence allows for accurate identifications, which are critical to building a solid case.
In many cases, the collected prints may be latent and partial, especially when it comes to fingerprints and palm prints. Latent prints are those that are not visible to the naked eye and require special techniques to be detected. This type of evidence requires careful analysis as it can be fragmentary and may correspond to one or more individuals.
Technicians must carry out detailed “one-to-one” comparisons to determine possible matches, which can be challenging when there is uncertainty about the number of people present at the scene. Proper collection and preservation of these samples are crucial in ensuring that the evidence remains valid and can be admitted in legal proceedings.
The importance of accuracy in evidence processing

Accurate identification and processing of evidence is essential to maintain the integrity of the judicial system. In criminal investigations, one of the most relevant types of evidence are biometric samples, especially fingerprints, which can be collected both at crime scenes and at forensic anatomical institutes to identify suspects or perform post-mortem identifications. Inaccurate collection or analysis of these samples can lead to serious miscarriages of justice, from the wrongful indictment of innocent people to the exoneration of the guilty, affecting both the victims and the credibility of the system.
Moreover, diligence is key in the analysis of evidence, in order for it to be considered irrefutable in trials. Lack of precision can make it difficult to link suspects to crime scenes due to insufficient evidence or issues with correctly identifying faces in images or videos. This risk also impacts the identification of deceased individuals or living persons through fingerprints, as insecure or slow methods can delay the investigation and hinder the effective resolution of cases. Accuracy not only facilitates the precise identification of individuals, but also strengthens public confidence in judicial proceedings and optimizes investigative resources.
The use of biometrics and its role in criminal investigation
Biometrics has profoundly transformed the approach to criminal investigations, providing advanced and accurate methods for suspect identification and evidence authentication. The ability to identify unique and unalterable characteristics of individuals, such as fingerprints, iris patterns or facial features, has greatly improved the accuracy of investigative processes. This technology streamlines procedures, optimizes the use of resources and reinforces the credibility of the judicial system by ensuring the authenticity of the evidence.
Today’s biometric software is specifically designed to assist forensic scientists in the collection and analysis of evidence in criminal investigations, offering multiple key applications:
- Identification of suspects and criminals: Through latent fingerprints and palm prints collected from various objects, these systems enable the fast and secure identification of individuals, even when the evidence is partial or fragmented.
- Identification of corpses: In forensic anatomy institutes and crime scenes, the software allows for quick and secure identification of bodies through fingerprints and palm prints, speeding up a critical process in investigations.
- Facial recognition from images or videos: In cases where there are photos or videos of suspects, facial biometrics provides an accurate and reliable means of identification, essential in scenarios where there are no physical prints.
- Identity verification of living individuals: By using fingerprints, iris and facial recognition, the software allows unequivocal verification of living individuals’ identity, even when there are doubts about their true identity, ensuring the authenticity of the identification in real time.
- Criminal case management: The software organizes and stores collected fingerprints, photos and videos, enabling efficient case management and ensuring that all evidence is available for analysis and eventual presentation at trial.
- Real-time interconnection: The technology allows real-time connections with other biometric databases (Civil Registry, Electoral Court, Prisons, Police, etc.), expanding the identification range and facilitating the pursuit for suspects through a more extensive search.
- International collaboration: Systems can exchange biometric data with international security agencies in appropriate formats and standards, contributing to the global fight against crime.
Discover Verázial ID Criminalistics our solution designed to ensure that every piece of evidence and every piece of data collected in criminal investigations can be used reliably.
Contact us for a demo and/or personalized assessment.
You May Also Like
You May Also Like