Problems using login and password as electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing
The use of the biometric electronic signature not only ensures data integrity and compliance with pharmaceutical regulations, but also solves the problems of inconvenience and loss of time and efficiency of employees.
Information systems in the pharmaceutical industry (MES, ERP, LIMS…) implement the various safety and quality measures needed for the manufacture of safe medicines, and compliance with the existing strict regulations regarding data integrity and traceability of tasks.
All the employees in the manufacturing processes perform the tasks assigned to them, usually managed in the manufacturing control software on a PC.
On this software they report the activity carried out and the characteristics inherent to this activity. At a certain point they must “sign” the activity report. So they must leave a record of which person is reporting which activity, keeping a clear tracking or traceability of each task performed by each employee.
Because, in compliance with pharmaceutical regulations, all processes in the medicines manufacturing processes must be signed by the responsible person. As for instance: the employee who performed a weighing, the chief pharmacist who verifies the dispensing and weighing of the medicine, and the quality assurance inspector who validates all weighings and their contents.
Most of these systems use the username plus the password as an electronic signature. In the previous article we explained the main problem of it: security problems in user identification that put data integrity at risk.
But it is not the only one, there are other important problems, which this article focuses on:
- Inconvenience for the employees using passwords.
- Loss of employee time in the identification.
- The IT team costs in password management.
- Risk of having to report on paper if passwords are forgotten.
Inconvenience for the employees using passwords
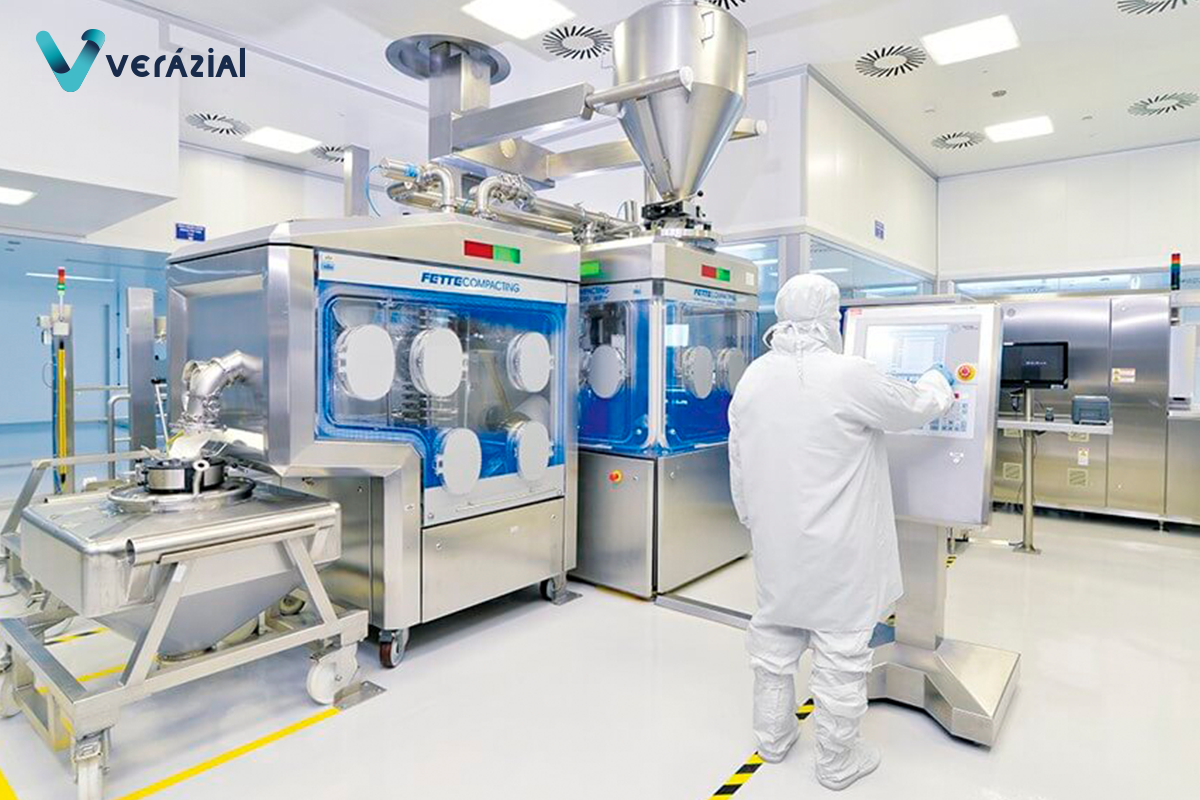
Manufacturing processes in the pharmaceutical industry require employees to protect themselves with gloves and hats, and in many cases, as in clean or sterile rooms, also masks and goggles (even in some cases “full-face” type) are needed.
In clean rooms, PCs may be embedded in the wall or encapsulated within stainless steel, to comply with pharmaceutical regulations and to be cleaned properly. They use a touch screen, without a keyboard or mouse, and with the appropriate protection to prevent any of the liquids or other substances used for cleaning the room from damaging the equipment.
The processes may require approximately between 30 and 60 minutes to be completed, and would require approximately 6 signatures between operators, supervisors and quality control. In a working day of 8 hours at each manufacturing station up to 96 signatures per day for user identification would be needed.
The employees have to enter their identification codes over and over again, between 40 and 80 times a day, depending on their job. And of course periodically change their passwords according to the company’s password policy.
In addition to the fact that they can make a mistake and enter wrong codes, having to re-enter them again. Passwords used under company password policies include quite a few characters and of various types, they are not usually simple.
Employees work with gloves on, and in many cases on touch screens, which increases inconvenience and the likelihood of errors.

Loss of employee time in the identification
Which they don’t use for their main tasks, the manufacturing itself. If we take into account an average of 15 seconds for each signature process with username and password, a user with an average of 50 signatures per day, would be wasting a total of 12.5 minutes a day in these processes, which makes 46 hours a year, more than a week of work a year lost in identifications per employee.
Or looking at it from the company’s economic side, one week of salary per year that the company loses. Or the opportunity cost of having manufactured medicines for one more week a year, which means having been able to have 2% more products manufactured.
The IT team costs in passwords management
The time IT employees must spend on supporting the use of passwords: definition of complexity, periodic renewal, changes due to user forgetfulness, control of password repetition, etc.
Risk of having to report on paper when a password is forgotten
In many cases manufacturing processes are 24×7, but the IT team’s work time usually has fewer hours. If manufacturing employees forget the password, and/or the system locks it due to multiple failed attempts, and it happens at a time when there is no IT colleague who can help reset it, the manufacturing employees will not be able to continue using the system.
This means that the users would not be able to sign the actions in the system, and the system could even prevent them from continuing using it without signing the last action, depending on how it is configured.
The company could have chosen 2 types of strategies:
- The computer system allows the employees to go ahead in the assigned tasks and sign them later. This would allow the employees to continue working, but it would be insecure, another person could be doing the work instead of the right employee for these tasks, who would be the one signing all of them the next day, for example.
- Forcing the employee to sign the processes on paper, which in addition to the additional insecurity inherent in the use of paper would need having to upload the reports to the production software the next day.
Is there any way to avoid these problems in electronic signatures?
Yes, and the solution is the same that avoids the main problem of using passwords, insecurity in identification, which was discussed in the previous article: the use of biometric identification as an electronic signature.
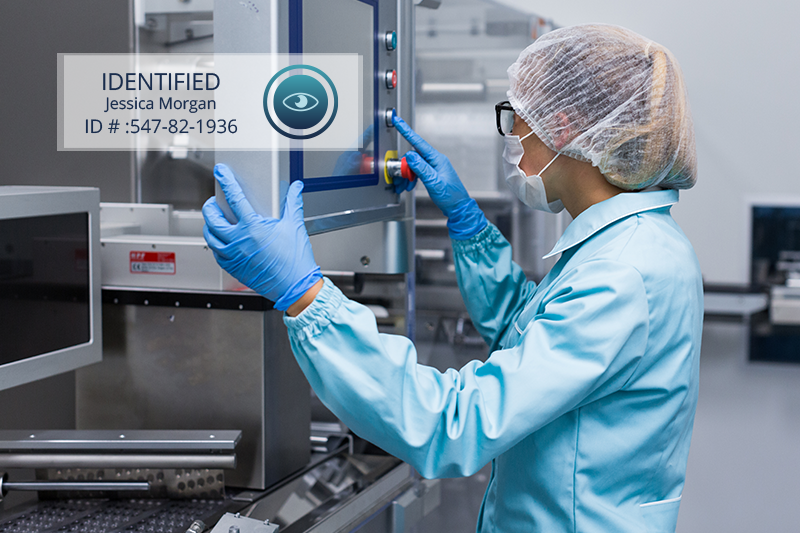
The user only has to look for a moment at a camera or iris sensor (or place the fingerprint on a fingerprint sensor in areas where they work without gloves), and the identification process occurs automatically. Therefore, the users don’t have to remember any passwords or change them periodically, nor do they have to enter characters every time they identify themselves, and they will never make a mistake when entering their identity.
The employee can dedicate more time to the actual manufacturing processes. Identification occurs very quickly, in less than 3 seconds. This saves the employee lot of time in the identification tasks that were performed with username and password.
The IT team has no need to manage passwords for the electronic signatures. The biometric samples are captured once to each user in a registration process, and from then on the employee will always be correctly identified. Without any maintenance work, as it was needed with the password system.
And of course, it will never happen that an employee depends on the IT team to continue working because of forgetting or blocking passwords.
In later articles on this blog we go into more detail on how to use biometric technologies as an electronic signature in drug manufacturing processes.
Find out how Verázial ID Pharma solves all employees’ identification problems in the pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Contact us for a demo and/or a customized analysis.
Referencias
- Foto de Toon Lambrechts en Unsplash
- Foto de Laurel and Michael Evans en Unsplash
Problems using login and password as electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing
The use of the biometric electronic signature not only ensures data integrity and compliance with pharmaceutical regulations, but also solves the problems of inconvenience and loss of time and efficiency of employees.
Information systems in the pharmaceutical industry (MES, ERP, LIMS…) implement the various safety and quality measures needed for the manufacture of safe medicines, and compliance with the existing strict regulations regarding data integrity and traceability of tasks.
All the employees in the manufacturing processes perform the tasks assigned to them, usually managed in the manufacturing control software on a PC.
On this software they report the activity carried out and the characteristics inherent to this activity. At a certain point they must “sign” the activity report. So they must leave a record of which person is reporting which activity, keeping a clear tracking or traceability of each task performed by each employee.
Because, in compliance with pharmaceutical regulations, all processes in the medicines manufacturing processes must be signed by the responsible person. As for instance: the employee who performed a weighing, the chief pharmacist who verifies the dispensing and weighing of the medicine, and the quality assurance inspector who validates all weighings and their contents.
Most of these systems use the username plus the password as an electronic signature. In the previous article we explained the main problem of it: security problems in user identification that put data integrity at risk.
But it is not the only one, there are other important problems, which this article focuses on:
- Inconvenience for the employees using passwords.
- Loss of employee time in the identification.
- The IT team costs in password management.
- Risk of having to report on paper if passwords are forgotten.
Inconvenience for the employees using passwords
Manufacturing processes in the pharmaceutical industry require employees to protect themselves with gloves and hats, and in many cases, as in clean or sterile rooms, also masks and goggles (even in some cases “full-face” type) are needed.
In clean rooms, PCs may be embedded in the wall or encapsulated within stainless steel, to comply with pharmaceutical regulations and to be cleaned properly. They use a touch screen, without a keyboard or mouse, and with the appropriate protection to prevent any of the liquids or other substances used for cleaning the room from damaging the equipment.
The processes may require approximately between 30 and 60 minutes to be completed, and would require approximately 6 signatures between operators, supervisors and quality control. In a working day of 8 hours at each manufacturing station up to 96 signatures per day for user identification would be needed.
The employees have to enter their identification codes over and over again, between 40 and 80 times a day, depending on their job. And of course periodically change their passwords according to the company’s password policy.
In addition to the fact that they can make a mistake and enter wrong codes, having to re-enter them again. Passwords used under company password policies include quite a few characters and of various types, they are not usually simple.
Employees work with gloves on, and in many cases on touch screens, which increases inconvenience and the likelihood of errors.

Loss of employee time in the identification
Which they don’t use for their main tasks, the manufacturing itself. If we take into account an average of 15 seconds for each signature process with username and password, a user with an average of 50 signatures per day, would be wasting a total of 12.5 minutes a day in these processes, which makes 46 hours a year, more than a week of work a year lost in identifications per employee.
Or looking at it from the company’s economic side, one week of salary per year that the company loses. Or the opportunity cost of having manufactured medicines for one more week a year, which means having been able to have 2% more products manufactured.
The IT team costs in passwords management
The time IT employees must spend on supporting the use of passwords: definition of complexity, periodic renewal, changes due to user forgetfulness, control of password repetition, etc.
Risk of having to report on paper when a password is forgotten
In many cases manufacturing processes are 24×7, but the IT team’s work time usually has fewer hours. If manufacturing employees forget the password, and/or the system locks it due to multiple failed attempts, and it happens at a time when there is no IT colleague who can help reset it, the manufacturing employees will not be able to continue using the system.
This means that the users would not be able to sign the actions in the system, and the system could even prevent them from continuing using it without signing the last action, depending on how it is configured.
The company could have chosen 2 types of strategies:
- The computer system allows the employees to go ahead in the assigned tasks and sign them later. This would allow the employees to continue working, but it would be insecure, another person could be doing the work instead of the right employee for these tasks, who would be the one signing all of them the next day, for example.
- Forcing the employee to sign the processes on paper, which in addition to the additional insecurity inherent in the use of paper would need having to upload the reports to the production software the next day.

Is there any way to avoid these problems in electronic signatures?
Yes, and the solution is the same that avoids the main problem of using passwords, insecurity in identification, which was discussed in the previous article: the use of biometric identification as an electronic signature.
The user only has to look for a moment at a camera or iris sensor (or place the fingerprint on a fingerprint sensor in areas where they work without gloves), and the identification process occurs automatically. Therefore, the users don’t have to remember any passwords or change them periodically, nor do they have to enter characters every time they identify themselves, and they will never make a mistake when entering their identity.
The employee can dedicate more time to the actual manufacturing processes. Identification occurs very quickly, in less than 3 seconds. This saves the employee lot of time in the identification tasks that were performed with username and password.
The IT team has no need to manage passwords for the electronic signatures. The biometric samples are captured once to each user in a registration process, and from then on the employee will always be correctly identified. Without any maintenance work, as it was needed with the password system.
And of course, it will never happen that an employee depends on the IT team to continue working because of forgetting or blocking passwords.
In later articles on this blog we go into more detail on how to use biometric technologies as an electronic signature in drug manufacturing processes.
Find out how Verázial ID Pharma solves all employees’ identification problems in the pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Contact us for a demo and/or a customized analysis.
Referencias
- Foto de Toon Lambrechts en Unsplash
- Foto de Laurel and Michael Evans en Unsplash
Problems using login and password as electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing
The use of the biometric electronic signature not only ensures data integrity and compliance with pharmaceutical regulations, but also solves the problems of inconvenience and loss of time and efficiency of employees.
Information systems in the pharmaceutical industry (MES, ERP, LIMS…) implement the various safety and quality measures needed for the manufacture of safe medicines, and compliance with the existing strict regulations regarding data integrity and traceability of tasks.
All the employees in the manufacturing processes perform the tasks assigned to them, usually managed in the manufacturing control software on a PC.
On this software they report the activity carried out and the characteristics inherent to this activity. At a certain point they must “sign” the activity report. So they must leave a record of which person is reporting which activity, keeping a clear tracking or traceability of each task performed by each employee.
Because, in compliance with pharmaceutical regulations, all processes in the medicines manufacturing processes must be signed by the responsible person. As for instance: the employee who performed a weighing, the chief pharmacist who verifies the dispensing and weighing of the medicine, and the quality assurance inspector who validates all weighings and their contents.
Most of these systems use the username plus the password as an electronic signature. In the previous article we explained the main problem of it: security problems in user identification that put data integrity at risk.
But it is not the only one, there are other important problems, which this article focuses on:
- Inconvenience for the employees using passwords.
- Loss of employee time in the identification.
- The IT team costs in password management.
- Risk of having to report on paper if passwords are forgotten.
Inconvenience for the employees using passwords
Manufacturing processes in the pharmaceutical industry require employees to protect themselves with gloves and hats, and in many cases, as in clean or sterile rooms, also masks and goggles (even in some cases “full-face” type) are needed.
In clean rooms, PCs may be embedded in the wall or encapsulated within stainless steel, to comply with pharmaceutical regulations and to be cleaned properly. They use a touch screen, without a keyboard or mouse, and with the appropriate protection to prevent any of the liquids or other substances used for cleaning the room from damaging the equipment.
The processes may require approximately between 30 and 60 minutes to be completed, and would require approximately 6 signatures between operators, supervisors and quality control. In a working day of 8 hours at each manufacturing station up to 96 signatures per day for user identification would be needed.
The employees have to enter their identification codes over and over again, between 40 and 80 times a day, depending on their job. And of course periodically change their passwords according to the company’s password policy.
In addition to the fact that they can make a mistake and enter wrong codes, having to re-enter them again. Passwords used under company password policies include quite a few characters and of various types, they are not usually simple.
Employees work with gloves on, and in many cases on touch screens, which increases inconvenience and the likelihood of errors.

Loss of employee time in the identification
Which they don’t use for their main tasks, the manufacturing itself. If we take into account an average of 15 seconds for each signature process with username and password, a user with an average of 50 signatures per day, would be wasting a total of 12.5 minutes a day in these processes, which makes 46 hours a year, more than a week of work a year lost in identifications per employee.
Or looking at it from the company’s economic side, one week of salary per year that the company loses. Or the opportunity cost of having manufactured medicines for one more week a year, which means having been able to have 2% more products manufactured.
The IT team costs in passwords management
The time IT employees must spend on supporting the use of passwords: definition of complexity, periodic renewal, changes due to user forgetfulness, control of password repetition, etc.
Risk of having to report on paper when a password is forgotten
In many cases manufacturing processes are 24×7, but the IT team’s work time usually has fewer hours. If manufacturing employees forget the password, and/or the system locks it due to multiple failed attempts, and it happens at a time when there is no IT colleague who can help reset it, the manufacturing employees will not be able to continue using the system.
This means that the users would not be able to sign the actions in the system, and the system could even prevent them from continuing using it without signing the last action, depending on how it is configured.
The company could have chosen 2 types of strategies:
- The computer system allows the employees to go ahead in the assigned tasks and sign them later. This would allow the employees to continue working, but it would be insecure, another person could be doing the work instead of the right employee for these tasks, who would be the one signing all of them the next day, for example.
- Forcing the employee to sign the processes on paper, which in addition to the additional insecurity inherent in the use of paper would need having to upload the reports to the production software the next day.

Is there any way to avoid these problems in electronic signatures?
Yes, and the solution is the same that avoids the main problem of using passwords, insecurity in identification, which was discussed in the previous article: the use of biometric identification as an electronic signature.
The user only has to look for a moment at a camera or iris sensor (or place the fingerprint on a fingerprint sensor in areas where they work without gloves), and the identification process occurs automatically. Therefore, the users don’t have to remember any passwords or change them periodically, nor do they have to enter characters every time they identify themselves, and they will never make a mistake when entering their identity.
The employee can dedicate more time to the actual manufacturing processes. Identification occurs very quickly, in less than 3 seconds. This saves the employee lot of time in the identification tasks that were performed with username and password.
The IT team has no need to manage passwords for the electronic signatures. The biometric samples are captured once to each user in a registration process, and from then on the employee will always be correctly identified. Without any maintenance work, as it was needed with the password system.
And of course, it will never happen that an employee depends on the IT team to continue working because of forgetting or blocking passwords.
In later articles on this blog we go into more detail on how to use biometric technologies as an electronic signature in drug manufacturing processes.
Find out how Verázial ID Pharma solves all employees’ identification problems in the pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Contact us for a demo and/or a customized analysis.
Referencias
- Foto de Toon Lambrechts en Unsplash
- Foto de Laurel and Michael Evans en Unsplash
You May Also Like
You May Also Like





