Biometric electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes
The use of biometrics in electronic signatures solves all the current problems with passwords in GMP regulated pharmaceutical manufacturing environments. But what technologies should we use? How should they be applied?
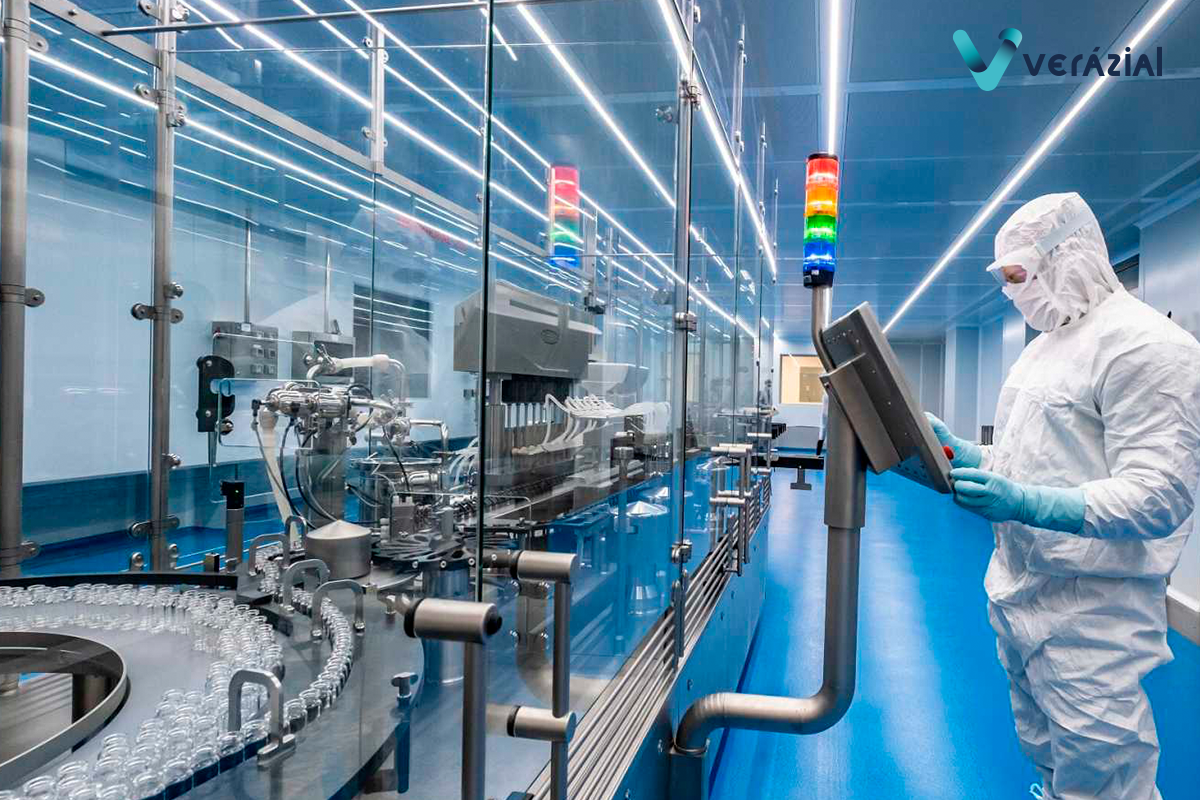
In compliance with pharmaceutical regulations in GMP environments, all processes in the medicines manufacturing processes must be signed by the responsible person. As for instance: the employee who performed a weighing, the chief pharmacist who verifies the dispensing and weighing of the medicine, and the quality assurance inspector who validates all weighings and their contents.
In 2 previous articles we explained it along with the regulations to ensure data integrity:
- Manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry: employees’ identification and data integrity
- Employees’ identification in the pharmaceutical industry according to ALCOA+
In pharmaceutical companies, employee authentication is carried out:
- through electronic signature with login and password, in processes with manufacturing software (MES, ERP, LIMS…)
- by handwritten signature on paper in companies that do not have their production control processes digitized.
The use of these identification methods cause the following problems:
1.- Security problems in the employee’s identification, that puts at risk the data integrity and thus the regulation compliance.
2.- Inconvenience for the employees using passwords or papers.
3.- Loss of employee time in the identification.
4.- The IT team costs in password management, or in the management of the paper based reports.
We explained these problems in following articles of the blog:
- Electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing: does it preserve data integrity and comply with regulations?
- Problems using login and password as electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
The right solution involves the use of biometric technologies as electronic signature, which the regulations themselves recognize as the most secure method.
Biometric technologies that can be applied
In the article “Introduction to applied biometrics” we explained the basic features of biometric technologies and the most important issues to take into consideration when applying them to business processes.

In the case of pharmaceutical manufacturing, it is essential to acquire a biometric system that can be easily integrated with the manufacturing software (MES, ERP, LIMS…), since all processes that should be signed are managed there.
The ergonomics of use in pharmaceutical manufacturing areas determine the biometric technologies that can be used:
- We cannot use fingerprint biometrics, because employees wear gloves.
- We also cannot use voice biometrics, because employees may be in a noisy environment and wearing masks. The use of voice biometrics in these cases is also a more inconvenient and time-consuming process.
- We can use facial biometrics in some areas where employees do not have too many occlusions. The most advanced current facial biometric technologies can allow the identification of employees wearing a mask, but when there are additional “full-face” type protective goggles or similar, it may not be used with security.
- Iris biometrics is contactless, and with the right iris sensors it is possible to capture irises through protective and full-face goggles, even with glasses underneath. Without any doubt, it is the most suitable biometric for greater security, speed and ease of use, especially in clean rooms.
Summarizing what biometric technologies can be used in the manufacturing areas: iris biometrics with complete reliability, and in some environments facial biometrics could also be applied.
What would the electronic signature process with biometrics be like?
A good biometric system will have:
- a server where the biometric database with samples of all employees is centralized;
- client software for the registration/enrollment of biometric samples of each employee;
- client software for identifying employees each time they need to sign a task;
- proper integration with production software (MES, ERP, etc.).
Let’s say we use iris biometrics, which is valid in all pharmaceutical manufacturing environments, even in clean room. The operation with any other biometric technology would be similar.
The use of the biometric system for electronic signatures would occur as follows:
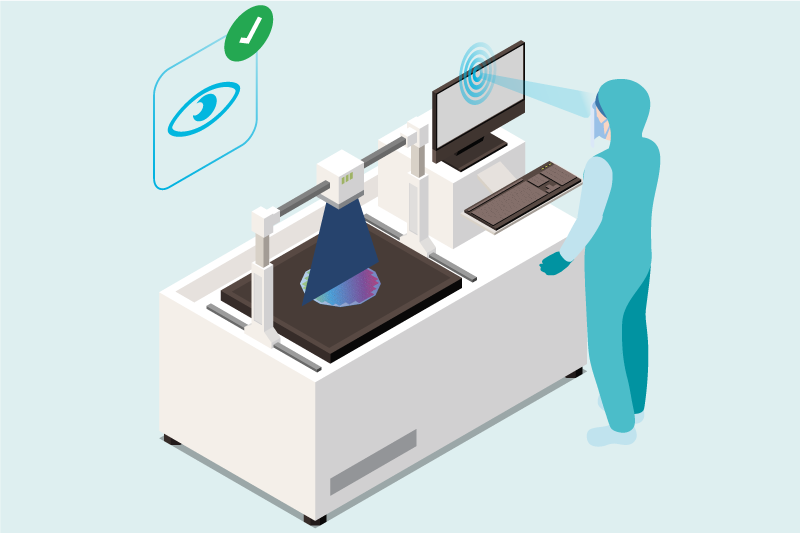
- Once for each employee, both irises are registered, usually in the administration or HR area. With an iris sensor connected to a USB port of one of the PCs and the biometric registration client software. From that moment on, the employee can be identified by the irises.
- An iris sensor will be connected via USB to each PC in the manufacturing area where the production software is running, as well as the identification client software of the biometric system that commands it. There are very convenient sensors that allow irises to be captured at a distance of about 30 – 40 cm.
- When the production software requires an electronic signature, the biometric identification client software integrated with the production software will be activated.
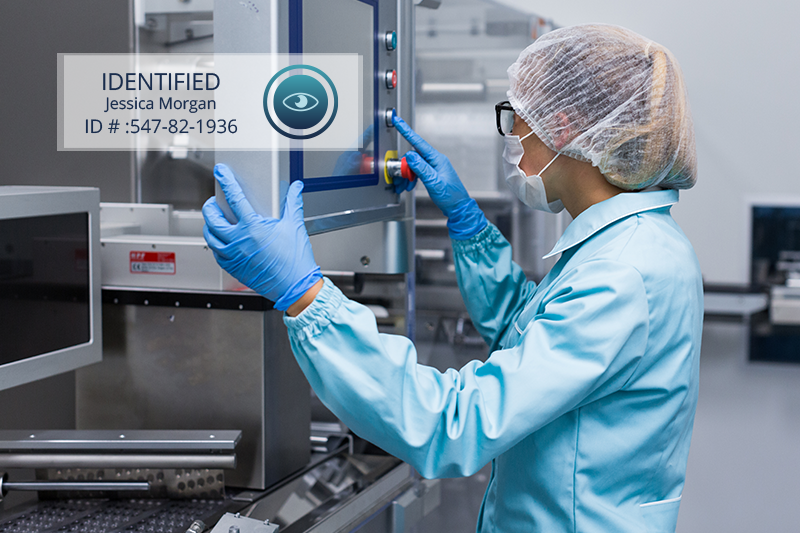
- The employee looks at the sensor for a second, and the image of the irises is captured, with which the biometric system securely identifies the employee.
- The production software receives the data from the identified person, and the operation is immediately signed, in a couple of seconds of total time throughout the entire process.
- There will be a double audit trail, on the one hand the existing one of the manufacturing software, and on the other hand the audit trail of the biometric system in which the identification occurred.
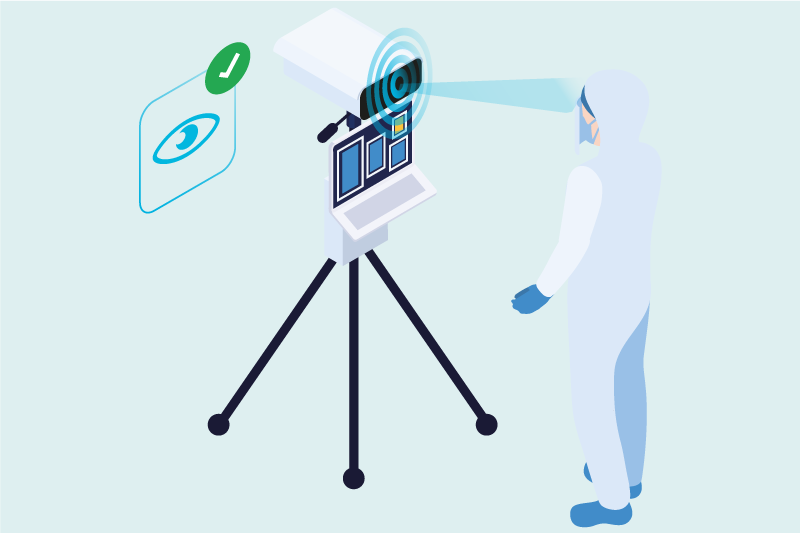
Benefits of the biometric electronic signature
The described operation solves all the problems of using passwords in electronic signatures. The use of biometrics for the electronic signatures of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes provides:
- 100% security in the identification of employees. Data integrity is ensured in terms of the identity of the employee who performs each task. There is no possibility that an employee can use the identity of another, it is impossible to take the irises of another employee to enter them into the system when reporting an activity. And the speed and ease of use allows the company to force all tasks to be signed, and one by one rather than in batches, which results in the maximum security in each regulated task.
- Ease of use and convenience. The user only has to look at the camera or iris sensor, and the identification process takes place automatically. Therefore, the users do not have to remember any passwords or change them periodically, nor do they have to enter characters each time they log in, and will never make a mistake when entering their identity.
- Improved efficiency. The employee can dedicate more time to the actual manufacturing processes. Identification occurs very quickly, in less than 3 seconds. This saves the employee around 40 hours per year in the identification tasks that were performed with username and password.
- Time saving for the IT team. No need to manage passwords for the electronic signatures. Each user’s 2 irises are captured once, in a registration process of less than 1 minute, and from then on he/she will always be correctly identified. Without any maintenance work, as it was needed with the password system.
Is biometrics only suited for electronic signatures in production areas?
Biometrics is suited for electronic signatures in any process in the pharmaceutical industry, not only in manufacturing areas that require greater control.
For instance, it would also be suitable for the electronic signatures of supervisors, when they are preparing a manufacturing guide, or for quality assurance managers when they are carrying out an internal audit. In this case, they could perform the signature with facial biometrics using their PC’s webcams, or with a connected fingerprint sensor, since they work in office environments where masks or gloves are not usually worn.
It is also advisable to use biometrics for physical and logical access according to the regulations. For example, to add maximum security without depending on passwords to use a chromatograph, which is controlled from a dedicated PC.
In future articles we will describe in more detail other processes in the pharmaceutical industry where the biometric signature is advisable, as well as elements where access to the system should be done with maximum biometric security.
Find out how Verázial ID Pharma solves all employees’ identification needs in the pharmaceutical companies.
Contact us for a demo and/or a customized analysis.
Biometric electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes
The use of biometrics in electronic signatures solves all the current problems with passwords in GMP regulated pharmaceutical manufacturing environments. But what technologies should we use? How should they be applied?
In compliance with pharmaceutical regulations in GMP environments, all processes in the medicines manufacturing processes must be signed by the responsible person. As for instance: the employee who performed a weighing, the chief pharmacist who verifies the dispensing and weighing of the medicine, and the quality assurance inspector who validates all weighings and their contents.
In 2 previous articles we explained it along with the regulations to ensure data integrity:
- Manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry: employees’ identification and data integrity
- Employees’ identification in the pharmaceutical industry according to ALCOA+
In pharmaceutical companies, employee authentication is carried out:
- through electronic signature with login and password, in processes with manufacturing software (MES, ERP, LIMS…)
- by handwritten signature on paper in companies that do not have their production control processes digitized.
The use of these identification methods cause the following problems:
1.- Security problems in the employee’s identification, that puts at risk the data integrity and thus the regulation compliance.
2.- Inconvenience for the employees using passwords or papers.
3.- Loss of employee time in the identification.
4.- The IT team costs in password management, or in the management of the paper based reports.
We explained these problems in following articles of the blog:
- Electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing: does it preserve data integrity and comply with regulations?
- Problems using login and password as electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
The right solution involves the use of biometric technologies as electronic signature, which the regulations themselves recognize as the most secure method.
Biometric technologies that can be applied
In the article “Introduction to applied biometrics” we explained the basic features of biometric technologies and the most important issues to take into consideration when applying them to business processes.

In the case of pharmaceutical manufacturing, it is essential to acquire a biometric system that can be easily integrated with the manufacturing software (MES, ERP, LIMS…), since all processes that should be signed are managed there.
The ergonomics of use in pharmaceutical manufacturing areas determine the biometric technologies that can be used:
- We cannot use fingerprint biometrics, because employees wear gloves.
- We also cannot use voice biometrics, because employees may be in a noisy environment and wearing masks. The use of voice biometrics in these cases is also a more inconvenient and time-consuming process.
- We can use facial biometrics in some areas where employees do not have too many occlusions. The most advanced current facial biometric technologies can allow the identification of employees wearing a mask, but when there are additional “full-face” type protective goggles or similar, it may not be used with security.
- Iris biometrics is contactless, and with the right iris sensors it is possible to capture irises through protective and full-face goggles, even with glasses underneath. Without any doubt, it is the most suitable biometric for greater security, speed and ease of use, especially in clean rooms.
Summarizing what biometric technologies can be used in the manufacturing areas: iris biometrics with complete reliability, and in some environments facial biometrics could also be applied.
What would the electronic signature process with biometrics be like?
A good biometric system will have:
- a server where the biometric database with samples of all employees is centralized;
- client software for the registration/enrollment of biometric samples of each employee;
- client software for identifying employees each time they need to sign a task;
- proper integration with production software (MES, ERP, etc.).
Let’s say we use iris biometrics, which is valid in all pharmaceutical manufacturing environments, even in clean room. The operation with any other biometric technology would be similar.
The use of the biometric system for electronic signatures would occur as follows:
- Once for each employee, both irises are registered, usually in the administration or HR area. With an iris sensor connected to a USB port of one of the PCs and the biometric registration client software. From that moment on, the employee can be identified by the irises.
- An iris sensor will be connected via USB to each PC in the manufacturing area where the production software is running, as well as the identification client software of the biometric system that commands it. There are very convenient sensors that allow irises to be captured at a distance of about 30 – 40 cm.
- When the production software requires an electronic signature, the biometric identification client software integrated with the production software will be activated.
- The employee looks at the sensor for a second, and the image of the irises is captured, with which the biometric system securely identifies the employee.
- The production software receives the data from the identified person, and the operation is immediately signed, in a couple of seconds of total time throughout the entire process.
- There will be a double audit trail, on the one hand the existing one of the manufacturing software, and on the other hand the audit trail of the biometric system in which the identification occurred.

Benefits of the biometric electronic signature
The described operation solves all the problems of using passwords in electronic signatures. The use of biometrics for the electronic signatures of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes provides:
- 100% security in the identification of employees. Data integrity is ensured in terms of the identity of the employee who performs each task. There is no possibility that an employee can use the identity of another, it is impossible to take the irises of another employee to enter them into the system when reporting an activity. And the speed and ease of use allows the company to force all tasks to be signed, and one by one rather than in batches, which results in the maximum security in each regulated task.
- Ease of use and convenience. The user only has to look at the camera or iris sensor, and the identification process takes place automatically. Therefore, the users do not have to remember any passwords or change them periodically, nor do they have to enter characters each time they log in, and will never make a mistake when entering their identity.
- Improved efficiency. The employee can dedicate more time to the actual manufacturing processes. Identification occurs very quickly, in less than 3 seconds. This saves the employee around 40 hours per year in the identification tasks that were performed with username and password.
- Time saving for the IT team. No need to manage passwords for the electronic signatures. Each user’s 2 irises are captured once, in a registration process of less than 1 minute, and from then on he/she will always be correctly identified. Without any maintenance work, as it was needed with the password system.
Is biometrics only suited for electronic signatures in production areas?
Biometrics is suited for electronic signatures in any process in the pharmaceutical industry, not only in manufacturing areas that require greater control.
For instance, it would also be suitable for the electronic signatures of supervisors, when they are preparing a manufacturing guide, or for quality assurance managers when they are carrying out an internal audit. In this case, they could perform the signature with facial biometrics using their PC’s webcams, or with a connected fingerprint sensor, since they work in office environments where masks or gloves are not usually worn.
It is also advisable to use biometrics for physical and logical access according to the regulations. For example, to add maximum security without depending on passwords to use a chromatograph, which is controlled from a dedicated PC.
In future articles we will describe in more detail other processes in the pharmaceutical industry where the biometric signature is advisable, as well as elements where access to the system should be done with maximum biometric security.
Find out how Verázial ID Pharma solves all employees’ identification needs in the pharmaceutical companies.
Contact us for a demo and/or a customized analysis.
Biometric electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes
The use of biometrics in electronic signatures solves all the current problems with passwords in GMP regulated pharmaceutical manufacturing environments. But what technologies should we use? How should they be applied?
In compliance with pharmaceutical regulations in GMP environments, all processes in the medicines manufacturing processes must be signed by the responsible person. As for instance: the employee who performed a weighing, the chief pharmacist who verifies the dispensing and weighing of the medicine, and the quality assurance inspector who validates all weighings and their contents.
In 2 previous articles we explained it along with the regulations to ensure data integrity:
- Manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry: employees’ identification and data integrity
- Employees’ identification in the pharmaceutical industry according to ALCOA+
In pharmaceutical companies, employee authentication is carried out:
- through electronic signature with login and password, in processes with manufacturing software (MES, ERP, LIMS…)
- by handwritten signature on paper in companies that do not have their production control processes digitized.
The use of these identification methods cause the following problems:
1.- Security problems in the employee’s identification, that puts at risk the data integrity and thus the regulation compliance.
2.- Inconvenience for the employees using passwords or papers.
3.- Loss of employee time in the identification.
4.- The IT team costs in password management, or in the management of the paper based reports.
We explained these problems in following articles of the blog:
- Electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing: does it preserve data integrity and comply with regulations?
- Problems using login and password as electronic signature in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
The right solution involves the use of biometric technologies as electronic signature, which the regulations themselves recognize as the most secure method.
Biometric technologies that can be applied
In the article “Introduction to applied biometrics” we explained the basic features of biometric technologies and the most important issues to take into consideration when applying them to business processes.

In the case of pharmaceutical manufacturing, it is essential to acquire a biometric system that can be easily integrated with the manufacturing software (MES, ERP, LIMS…), since all processes that should be signed are managed there.
The ergonomics of use in pharmaceutical manufacturing areas determine the biometric technologies that can be used:
- We cannot use fingerprint biometrics, because employees wear gloves.
- We also cannot use voice biometrics, because employees may be in a noisy environment and wearing masks. The use of voice biometrics in these cases is also a more inconvenient and time-consuming process.
- We can use facial biometrics in some areas where employees do not have too many occlusions. The most advanced current facial biometric technologies can allow the identification of employees wearing a mask, but when there are additional “full-face” type protective goggles or similar, it may not be used with security.
- Iris biometrics is contactless, and with the right iris sensors it is possible to capture irises through protective and full-face goggles, even with glasses underneath. Without any doubt, it is the most suitable biometric for greater security, speed and ease of use, especially in clean rooms.
Summarizing what biometric technologies can be used in the manufacturing areas: iris biometrics with complete reliability, and in some environments facial biometrics could also be applied.
What would the electronic signature process with biometrics be like?
A good biometric system will have:
- a server where the biometric database with samples of all employees is centralized;
- client software for the registration/enrollment of biometric samples of each employee;
- client software for identifying employees each time they need to sign a task;
- proper integration with production software (MES, ERP, etc.).
Let’s say we use iris biometrics, which is valid in all pharmaceutical manufacturing environments, even in clean room. The operation with any other biometric technology would be similar.
The use of the biometric system for electronic signatures would occur as follows:
- Once for each employee, both irises are registered, usually in the administration or HR area. With an iris sensor connected to a USB port of one of the PCs and the biometric registration client software. From that moment on, the employee can be identified by the irises.
- An iris sensor will be connected via USB to each PC in the manufacturing area where the production software is running, as well as the identification client software of the biometric system that commands it. There are very convenient sensors that allow irises to be captured at a distance of about 30 – 40 cm.
- When the production software requires an electronic signature, the biometric identification client software integrated with the production software will be activated.
- The employee looks at the sensor for a second, and the image of the irises is captured, with which the biometric system securely identifies the employee.
- The production software receives the data from the identified person, and the operation is immediately signed, in a couple of seconds of total time throughout the entire process.
- There will be a double audit trail, on the one hand the existing one of the manufacturing software, and on the other hand the audit trail of the biometric system in which the identification occurred.

Benefits of the biometric electronic signature
The described operation solves all the problems of using passwords in electronic signatures. The use of biometrics for the electronic signatures of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes provides:
- 100% security in the identification of employees. Data integrity is ensured in terms of the identity of the employee who performs each task. There is no possibility that an employee can use the identity of another, it is impossible to take the irises of another employee to enter them into the system when reporting an activity. And the speed and ease of use allows the company to force all tasks to be signed, and one by one rather than in batches, which results in the maximum security in each regulated task.
- Ease of use and convenience. The user only has to look at the camera or iris sensor, and the identification process takes place automatically. Therefore, the users do not have to remember any passwords or change them periodically, nor do they have to enter characters each time they log in, and will never make a mistake when entering their identity.
- Improved efficiency. The employee can dedicate more time to the actual manufacturing processes. Identification occurs very quickly, in less than 3 seconds. This saves the employee around 40 hours per year in the identification tasks that were performed with username and password.
- Time saving for the IT team. No need to manage passwords for the electronic signatures. Each user’s 2 irises are captured once, in a registration process of less than 1 minute, and from then on he/she will always be correctly identified. Without any maintenance work, as it was needed with the password system.
Is biometrics only suited for electronic signatures in production areas?
Biometrics is suited for electronic signatures in any process in the pharmaceutical industry, not only in manufacturing areas that require greater control.
For instance, it would also be suitable for the electronic signatures of supervisors, when they are preparing a manufacturing guide, or for quality assurance managers when they are carrying out an internal audit. In this case, they could perform the signature with facial biometrics using their PC’s webcams, or with a connected fingerprint sensor, since they work in office environments where masks or gloves are not usually worn.
It is also advisable to use biometrics for physical and logical access according to the regulations. For example, to add maximum security without depending on passwords to use a chromatograph, which is controlled from a dedicated PC.
In future articles we will describe in more detail other processes in the pharmaceutical industry where the biometric signature is advisable, as well as elements where access to the system should be done with maximum biometric security.
Find out how Verázial ID Pharma solves all employees’ identification needs in the pharmaceutical companies.
Contact us for a demo and/or a customized analysis.
You May Also Like
You May Also Like





